In the current business landscape, where corporations are held accountable by various entities such as the media, public, and advocacy groups, being genuine is the most important factor in maintaining a positive public image. The level of authenticity a company exhibits is determined by its goals, values, and ability to generate profits, which in turn affects its potential for growth, including attracting investors and support from other organizations, as well as expanding its workforce.
Stakeholders, such as investors and employees, play a significant role in a company’s success. These individuals or groups have a vested interest in the business’s performance. Therefore, organizations must establish healthy and well-balanced relationships with their stakeholders to maintain their authenticity and meet their expectations.
Read on to find out more about the types of stakeholders and their roles.
what’s in the article
- Types of Stakeholders
- The Roles of Different Categories Of Stakeholders
- Why Are Stakeholders Important?
- A Checklist of Questions for a Stakeholder
- Conclusion
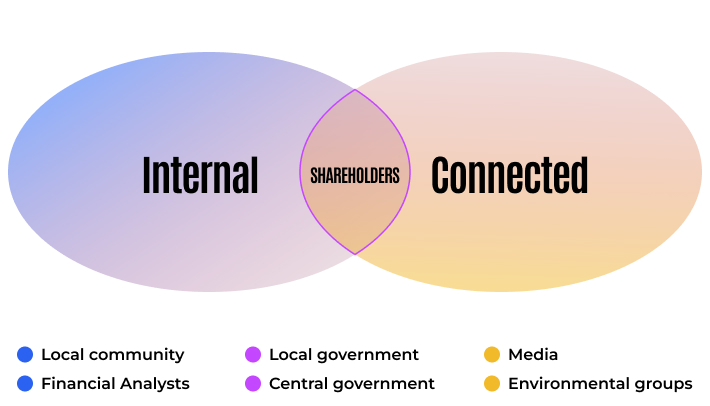
Types of Stakeholders
Stakeholders in business are individuals, groups, or organizations that have an interest in the success or failure of a business. They can be internal or external to the company, and their interests can be diverse.
External stakeholders
An external stakeholder is an individual or organization that has a vested interest in the performance of a company but is not part of its internal operations. These stakeholders can include customers, suppliers, investors, creditors, regulators, and even the community in which the company operates.
External stakeholders often have an impact on the success or failure of a company, as their actions or opinions can influence the business’s reputation, financial stability, and overall success. For example, customers who have a positive experience with a company are likely to become repeat customers and recommend the company to others, while negative experiences can lead to a loss of business and damage to the company’s brand.
Suppliers, on the other hand, can affect a company’s supply chain and production capabilities. The actions of investors and creditors can impact a company’s financial stability, while regulators can influence the company’s compliance with laws and regulations.
Besides, companies need to identify and understand their stakeholders’ obligations concerning the protection and use of personal data and stick to GDPR. This includes employees, customers, vendors, and partners. By doing so, companies can ensure that they comply with GDPR requirements and avoid hefty fines and legal actions.
Customers are crucial stakeholders as they purchase the company’s products or services, and their satisfaction and loyalty are essential for the success of the company. Suppliers are also important stakeholders as they provide the company with the necessary raw materials or services to carry out its operations. Investors are individuals or groups that provide funding to the company, and their investment is crucial for the company’s growth and expansion. Regulators are responsible for ensuring that the company complies with the relevant laws and regulations, and their approval is necessary for the company to operate.
Internal stakeholders
Internal stakeholders in a business are individuals within the organization who have a direct impact on the company’s operations and decision-making. Employees, managers, and shareholders are examples of internal stakeholders.
Employees as stakeholders share responsibility for carrying out the day-to-day activities of the organization and have a direct impact on the success of the company. Managers are responsible for overseeing employees and ensuring that the organization is operating effectively. Shareholders own a portion of the company and have a vested interest in its performance, profitability, and growth.
Primary stakeholders
Employees as stakeholders rely on the company for their livelihoods and are directly affected by the company’s decisions regarding salaries, benefits, and working conditions. Customers are directly impacted by the quality of the products or services provided by the company, and suppliers rely on the company for business and revenue.
Secondary stakeholders
Secondary stakeholders are individuals or groups that are indirectly affected by the company’s actions and decisions. The media, advocacy groups, and the community are examples of secondary stakeholders. The media can influence public opinion and perception of the company through its reporting and coverage. Advocacy groups may raise concerns about the company’s impact on the environment or society. The community may be impacted by the company’s operations or decisions.
Key stakeholders
Key stakeholders are individuals or groups that have a significant impact on the company’s success or failure. Major investors, customers, or regulators are examples of key stakeholders. Major investors provide significant funding to the company and may have a say in important decisions or actions taken by the company. Customers that account for a significant portion of the company’s revenue or are influential in the industry are also considered key stakeholders. Regulators that have the power to approve or deny the company’s operations or actions are also key stakeholders.
Influential stakeholders
Influential stakeholders are individuals or groups that have the ability to influence the opinions and actions of other stakeholders. Industry experts or thought leaders are examples of influential stakeholders. These stakeholders may have significant expertise or credibility in the industry and may sway the opinions of other stakeholders, such as customers or investors, through their endorsements or opinions.
The Roles of Different Categories Of Stakeholders
Stakeholders are individuals or groups that have a vested interest in the success or failure of an organization. Understanding the roles of different categories of stakeholders is crucial for any organization to thrive. Below, we will discuss the stakeholders roles and responsibilities.
Internal Stakeholders
Internal stakeholders’ roles can vary depending on their positions in the organization, but they all share a common interest in the organization’s success. Employees, for instance, play a crucial role in the success of any organization. They are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day operations, delivering products and services, and ensuring customer satisfaction. Management, on the other hand, is responsible for setting the organization’s goals, developing strategies, and ensuring that employees are working efficiently towards achieving those goals.
External Stakeholders
If we define external stakeholders, their roles can vary, but they all have an impact on the organization’s success. Customers, for example, are essential stakeholders for any organization. They are the primary source of revenue, and their satisfaction is crucial to the company’s growth. Suppliers, on the other hand, provide the organization with the necessary resources to deliver its products or services. They have a significant impact on the organization’s supply chain and can impact its performance.
Primary Stakeholders
Primary stakeholders’ roles are crucial in shaping the organization’s success, and their interests must be taken into account when making decisions. For example, customers’ interests must be taken into account when developing new products or services. Shareholders’ interests must be taken into account when making decisions that affect the organization’s financial performance. The local community’s interests must be taken into account when making decisions that affect the environment or the community’s well-being.
Secondary Stakeholders
Their roles are essential in shaping the organization’s reputation and can impact its success. For instance, the media can impact an organization’s reputation by reporting negative news. Government agencies can impact an organization’s success by imposing regulations that affect its operations. Competitors can impact an organization’s success by offering better products or services.
Key Stakeholders
Key stakeholders’ roles are crucial in shaping the organization’s long-term success, and their interests must be taken into account when making strategic decisions. For instance, top executives’ interests must be taken into account when making decisions that affect the organization’s leadership. Major shareholders’ interests must be taken into account when making decisions that affect the organization’s financial performance. Strategic partners’ interests must be taken into account when making decisions that affect the organization’s partnerships.
Influential Stakeholders
Influential stakeholders’ roles are crucial in shaping public opinion and can impact an organization’s success. For instance, government officials can influence an organization’s success by passing laws or regulations that affect its operations.

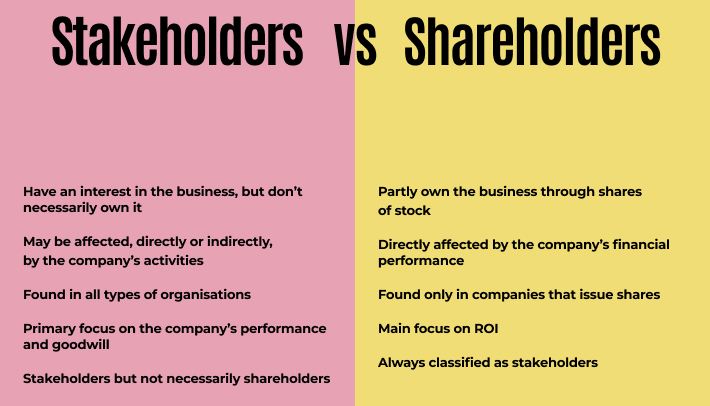
Stakeholders vs. Shareholders
Stakeholders and shareholders are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing. Understanding the difference between stakeholders and shareholders is crucial for any organization to thrive. In this article, we will discuss the differences between stakeholders and shareholders and their roles in an organization.
While stakeholders and shareholders both have an interest in an organization’s success, their interests and priorities can sometimes conflict with each other. Stakeholders prioritize the organization’s impact on society and the environment, while shareholders prioritize financial performance.
Stakeholders have a broader range of interests than shareholders, as they are not limited to those who have a financial interest in the organization. Stakeholders can include employees, customers, suppliers, the local community, and the government. Shareholders, on the other hand, are limited to those who own a portion of the organization’s stock or shares.
Stakeholders and shareholders both have a significant impact on an organization’s success. Therefore, it is essential for organizations to balance the interests of both stakeholders and shareholders when making decisions that affect the organization. This requires a thorough understanding of the needs and priorities of all stakeholders, as well as the ability to make strategic decisions that align with the organization’s mission and values.
Why Are Stakeholders Important?
Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have a vested interest in an organization’s success or failure. They can include employees, customers, suppliers, the local community, and the government. Stakeholders play a critical role in an organization’s success, and understanding why they are important is crucial for any organization to thrive.
Here are some reasons why stakeholders are important.
They can impact an organization’s reputation
It affects the organization’s financial performance. For example, if an organization is perceived as socially responsible, it can attract more customers and employees. However, if an organization is perceived as unethical, it can lose customers and employees, which can hurt its financial performance.
They can provide valuable feedback
Stakeholders can help improve an organization’s products or services. For example, customers can provide feedback on product quality and service, while employees can provide feedback on workplace conditions and processes.
Stakeholders can provide resources
They can provide an organization with funding, expertise, and networks. For example, investors can provide funding to an organization, while suppliers can provide expertise on the latest technologies.
Stakeholders can influence decision-making
The government can influence an organization’s decisions through regulations, while employees can influence an organization’s decisions through collective bargaining.
They can hold an organization accountable
If an organization is not fulfilling its social or environmental responsibilities, stakeholders can hold it accountable through boycotts, protests, or legal action.
A Checklist of Questions for a Stakeholder
Here are some questions that a stakeholder can use to evaluate their understanding of the company’s strategic goals and centralized tracking of key indicators:
- How will the company use the data collected from tracking key indicators to inform future decision-making?
- What are the main strategic goals of the company and how do they align with our advice?
- How will the centralized tracking of key indicators help the company achieve its strategic goals?
- Can you name some of the key indicators that will be tracked and how they are relevant to the company’s goals?
- How will the company measure progress towards its strategic goals using the tracked indicators?
- What role can you play as a stakeholder to support the company in achieving its strategic goals?
- Can you provide an example of how our advice on identifying strategic goals and tracking key indicators has been implemented in the company?
- How will the company communicate progress towards its strategic goals to stakeholders, including employees and investors?
- What potential challenges do you anticipate the company facing in implementing this strategy, and how can they be addressed?
- How will the company ensure that the tracking of key indicators remains relevant and effective over time?
Conclusion
Now you are more aware of the types of stakeholders and their roles. Stakeholders play a crucial role in the success of an organization. Understanding the different types of stakeholders and their functions can help organizations prioritize and effectively manage their relationships with them.
By engaging with stakeholders and addressing their needs and concerns, organizations can build strong relationships that benefit everyone involved. Overall, recognizing the importance of stakeholders and their functions can help organizations make informed decisions and achieve their goals more effectively.

About author
Roman Bondarenko is the CEO of EVNE Developers. He is an expert in software development and technological entrepreneurship and has 10+years of experience in digital transformation consulting in Healthcare, FinTech, Supply Chain and Logistics.
Author | CEO EVNE Developers